In this position the ultrasound beam (light blue) cuts the heart through the pulmonary artery and pulmonic valve.

This is how the view looks in a still frame and cartoon


This is a video clip of an ideal view
Doppler
In this view you will want to use color Doppler and PW/CW as needed to assess for pulmonic valve pathology as shown below.
Diastole

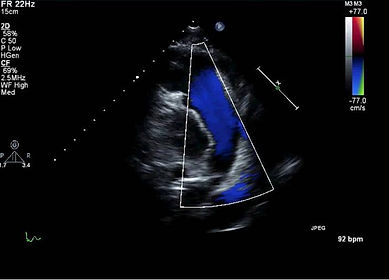
Systole
PW and CW Doppler will allow you to measure the RV outflow tract velocities and assess severity of pulmonic stenosis and insufficiency.
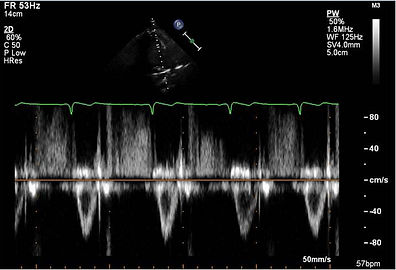
PW Doppler

CW Doppler
With CW Doppler the pulmonic insufficiency (PI) jet can help you estimate the pulmonary artery diastolic pressure (PAD) using 4V^2 plus the RA pressure. Here the velocity is 1m/s so it would be 4mmHg plus the RA pressure. The same can be done in the parasternal short axis view of this structure
